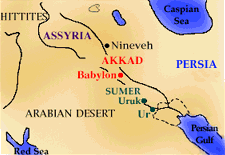

Civilization in Mesopotamia developed in city states; Uruk and Ur were among the most prominent ones. The Sumer kingdom brought several of them under unified control.
Babylon developed as a provincial centre of the kingdom of Ur. It became the capital of a small independent kingdom in 1894 BC, which conquered the surrounding city-states during the reign of Hammurabi (1792-1750 BC). Babylon then became the capital of the country known as Babylonia, which included southern Mesopotamia and parts of Assyria.
Babylon's power declined after a few centuries, but in the 7th and 6th centuries BC it recovered and reached its greatest height. Its extensive ruins on the banks of the Euphrates River can still be seen about 88 kilometres south of Baghdad, Iraq.