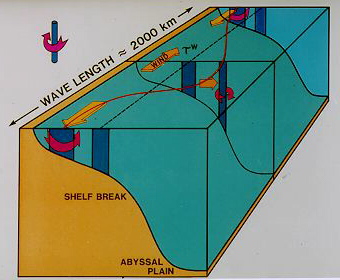
The effect of variable wind stress on the coastal ocean, demonstrated for a shelf in the southern hemisphere. The surface mixed layer is now removed from the diagram, and only the water below the mixed layer is shown.
Northward wind stress produces downwelling and pushes the water below the mixed layer away from the coast. Southward wind stress produces upwelling and pulls the water below the mixed layer towards the coast.
As a result, water that originally was located at the broken line that runs parallel to the coast is moved into the location shown by the red line. A water column on the central section that was originally located under the broken line is moved into deeper water and gains negative vorticity; the water columns originally located under the broken line at both ends of the diagram are moved into shallower water and gain positive vorticity.
contact address: